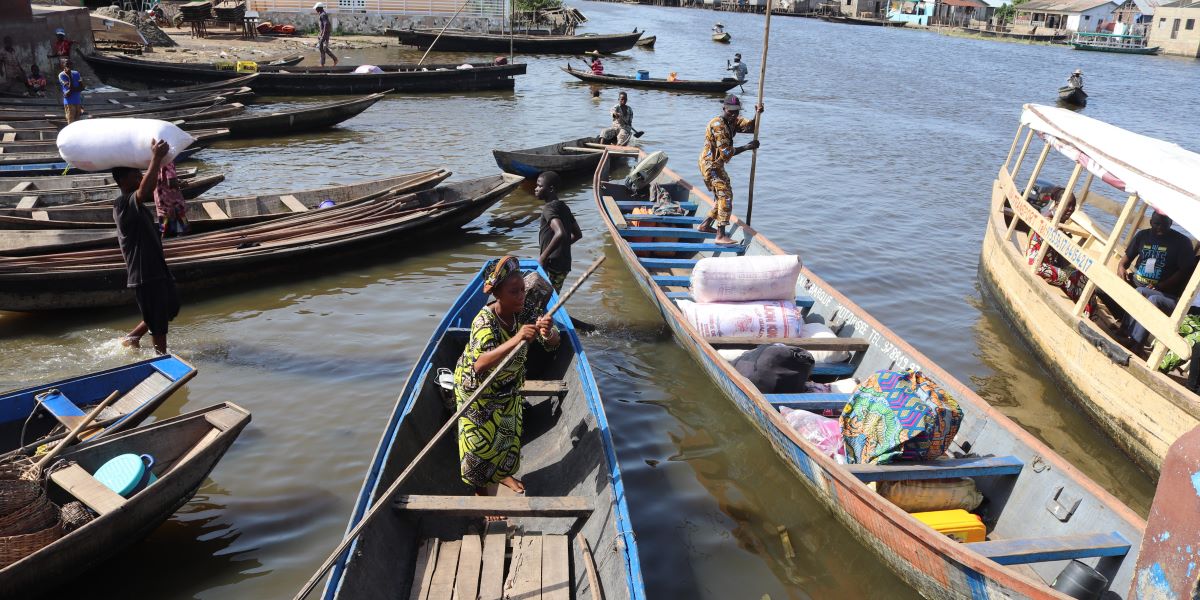
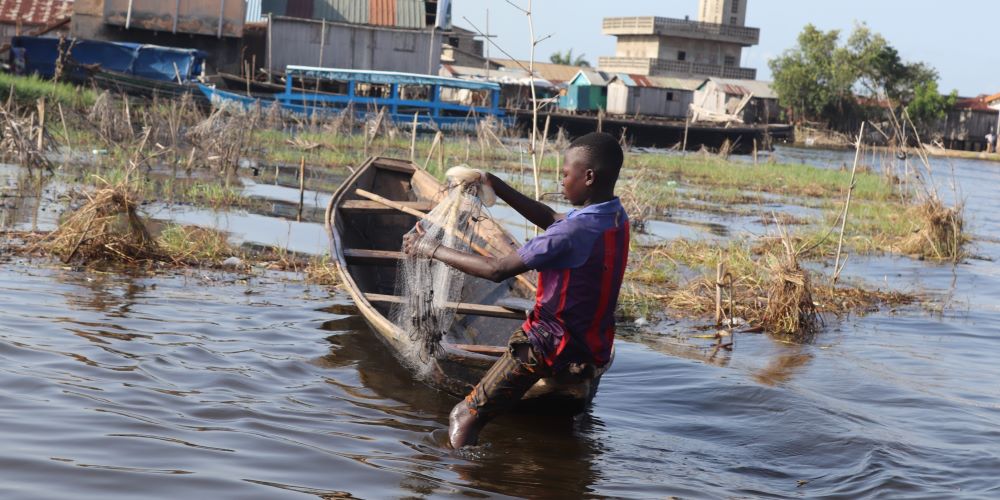
Several initiatives have been launched in Benin to promote inland fishing. These include training fishermen, raising awareness of sustainable practices, modernising equipment, scientific research and developing aquaculture to diversify fish sources.
Several initiatives have been launched in Benin to promote inland fishing. These include training fishermen, raising awareness of sustainable practices, modernising equipment, scientific research and developing aquaculture to diversify fish sources.
Current challenges facing inland fishing in Benin
The major challenges facing inland fishing in Benin include:
– The degradation of the river-lagoon environment.
– The appearance and proliferation of floating vegetation.
– Strong demographic pressure.
– Over-exploitation of fishery resources.
– Increased fishing effort, leading to a reduction in catches and yields.
– Widespread use of fishing gear that does not comply with regulations.
– Socio-professional conflicts linked to the appropriation of bodies of water.
– The threat of pollution of aquatic ecosystems.
– Difficulties in processing, preserving and marketing fishery products.
Prospects for inland fishing in Benin
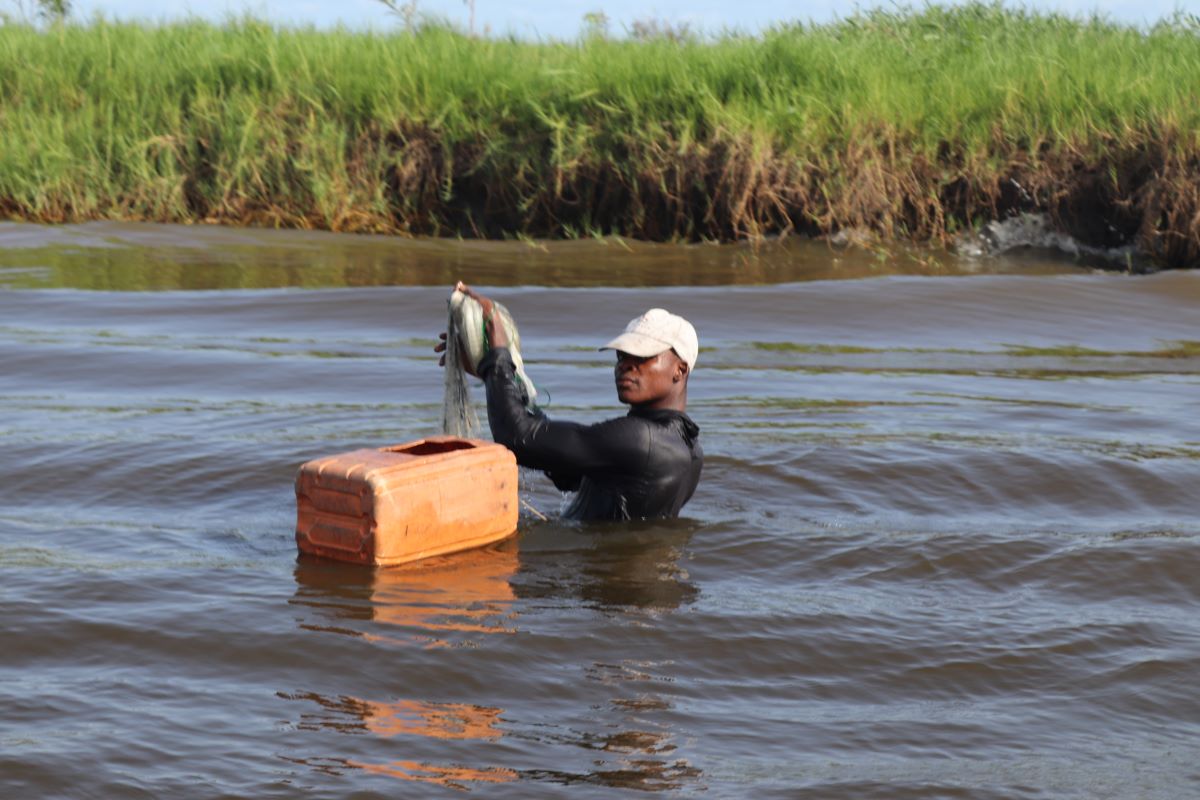 To overcome these challenges, some encouraging prospects are envisaged:
To overcome these challenges, some encouraging prospects are envisaged:
– Promoting sustainable fishing practices to preserve aquatic resources and the ecological balance.
– Develop small-scale aquaculture to diversify production and contribute to food security.
– To disseminate the voluntary guidelines for small-scale fishing throughout the country.
– Invest in training for fishermen to improve their skills and productivity.
– Implement aquatic resource management policies to prevent over-exploitation.
– Strengthen the fishing value chain from catch to market.
– Collaborate with other countries on regional fisheries management initiatives and facilitate cross-border trade.
– Adapt fishing communities to climate change.
Inland fishing is a crucial socio-economic pillar in Benin. However, its challenges persist, hindering its harmonious development. These challenges must be tackled if the sub-sector is to achieve its full potential and make a significant contribution to the national economy and food security.
By FeNaPA-BENIN (President Louis Victor AMETEPE) – January 2024